Introduction
Developing and executing effective marketing strategies is crucial for growth in the competitive consumer goods sector. The market demands a plan and a comprehensive approach integrating various data sources and strategic elements. This article proposes a robust and comprehensive model that synthesizes external and internal data stacks, brand strategy, and the 4Ps of marketing to achieve successful marketing execution.
Overview of the Model
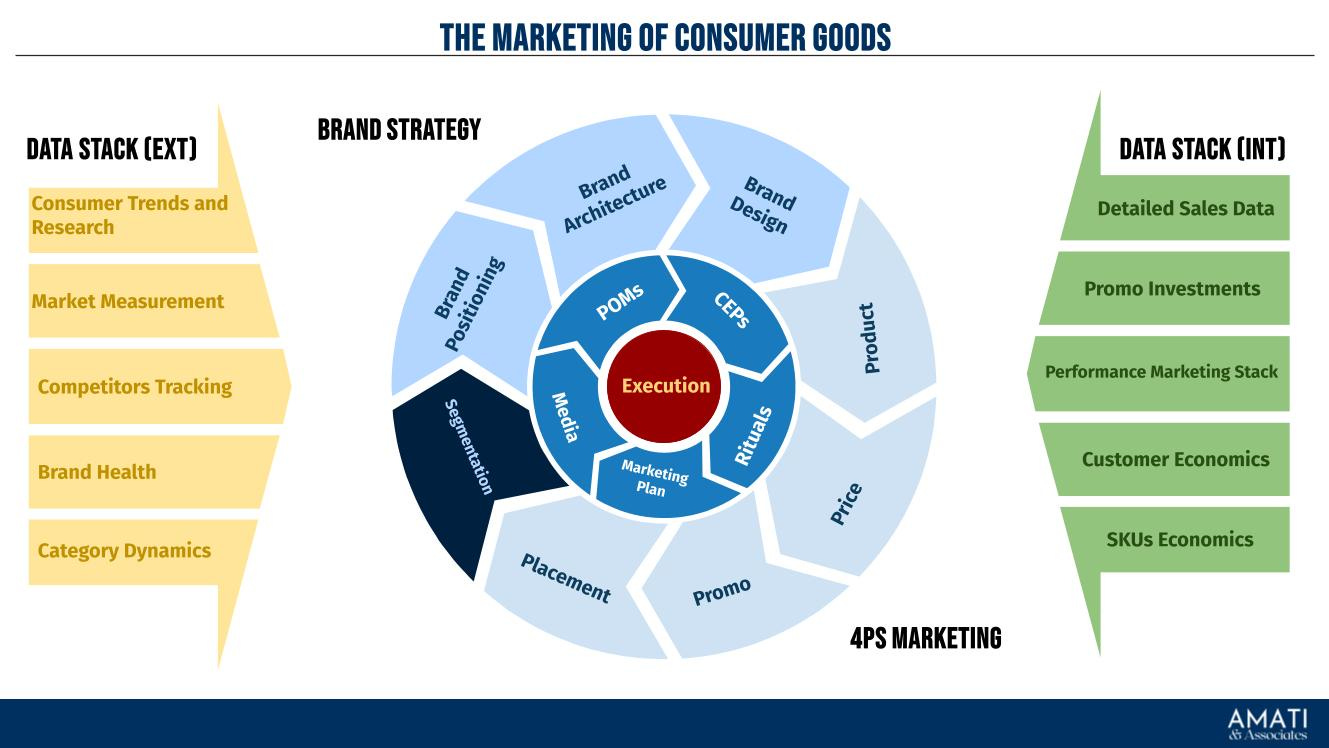
This marketing model is a theoretical construct and a practical guide structured around three primary components: External Data Stack, Internal Data Stack, Brand Strategy, and 4Ps Marketing. Each element is crucial in creating a cohesive marketing plan centered on execution. The model aims to provide a clear and practical pathway from data collection to strategy formulation and execution, making it a valuable tool for any marketing professional.
Data Stack (External)
The external data stack comprises several vital elements for understanding the market environment and consumer behavior.
Consumer Trends and Research: Staying attuned to consumer behavior and emerging market trends is vital. This involves continuous research and analysis of consumers' needs and preferences, providing insights that inform product development and marketing strategies. For instance, a company like Procter & Gamble conducts extensive consumer research to understand current trends in household products, enabling them to innovate and stay ahead of competitors. They also monitor weak signals and assess the long-term impact of emerging trends driven by demographic, social, and cultural changes.
Market Measurement: This involves tracking market performance through various metrics and indicators. Understanding market size, growth rates, and market share helps in strategic planning and identifying opportunities for expansion or improvement. An example would be how Coca-Cola uses market measurement to monitor the performance of its beverage products across different regions, allowing it to adapt its strategies accordingly. Market measurements are traditionally heavy on modern trade and become less and less reliable when built around other channels. Nevertheless, it is fundamental to monitor across channels.
Competitors Tracking: Keeping an eye on competitors is essential to remain competitive. This includes monitoring their marketing strategies, product launches, and overall market behavior.
Brand Health: Assessing brand health involves measuring brand awareness, perception, and loyalty. Key metrics include Net Promoter Score (NPS), brand equity monitors, and customer satisfaction scores. Understanding brand health helps maintain a strong brand image and identify areas for improvement. An example is Nike, which regularly assesses its brand health to ensure it remains a leading brand in sportswear. Brand Health Monitors also tell us whether the consumers perceive the brand as marketers would expect.
Category Dynamics: Understanding the dynamics within product categories provides insights into consumer preferences and trends. This involves analyzing category growth, penetration, frequency of purchase, and other competitive dynamics. For example, P&G, Unilever, and Reckitt analyze category dynamics to monitor the basket of choice and switching analysis, volume source, and promotional activities effectiveness.
Data Stack (Internal)
The internal data stack is crucial in informing marketing strategies and decisions. By leveraging internal data sources, you can gain valuable insights into consumer behavior, product performance, and market trends, which are crucial for making informed marketing decisions and optimizing strategies.
Detailed Sales Data: Analyzing sales data provides insights into consumer behavior, product performance, and market trends. This information is crucial for making informed marketing decisions and optimizing strategies. For instance, most consumer companies use detailed sales data to track product performance, manage inventory, and plan promotional campaigns.
Promo Investments: Tracking promotional investments helps understand various promotional activities' return on investment (ROI). These data must be combined with market measurement and statistical modeling to track the effectiveness of promotional campaigns and return on sales. Of course, the data layer must include an attribution model to link all data sources together.
Performance Marketing Stack: Leveraging tools and technologies in performance marketing optimizes marketing efforts. This includes data analytics, marketing automation, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems. Salesforce provides a comprehensive performance marketing stack that helps businesses manage customer relationships and optimize marketing campaigns.
Customer Economics: Understanding customer lifetime value (CLV) and acquisition costs helps make strategic investment decisions. This involves analyzing the profitability of different customer segments and optimizing marketing spend. For example, Amazon calculates the CLV of its Prime members to determine the value of investing in membership benefits and marketing campaigns to acquire and retain these customers.
SKUs Economics: Efficiently managing product variations (SKUs) is crucial for profitability. This involves analyzing the performance of different SKUs and making informed decisions about product offerings. For instance, Unilever manages the economics of its various SKUs by analyzing sales data and consumer preferences and optimizing its product portfolio for profitability.
Brand Strategy
A strong brand strategy is the backbone of successful marketing. This component of the model includes several critical elements:
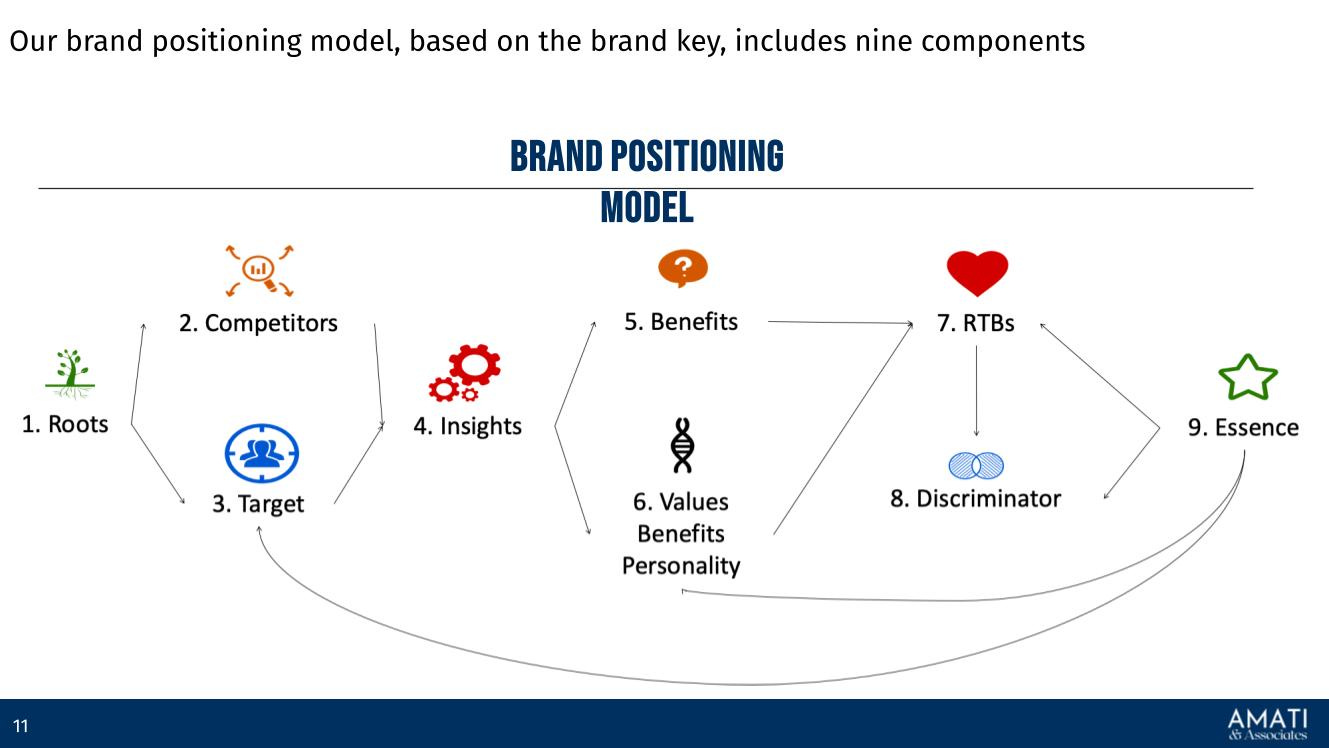
Brand Positioning: Brand positioning is the strategic process of defining and establishing a brand's unique place in the market and the minds of consumers. It differentiates the brand from competitors by highlighting its distinctive attributes, benefits, and values. Brand positioning aims to create a clear, concise, and compelling perception of the brand that resonates with the target audience. Very often, the brand essence is defined in terms of purpose. In other cases, it is in terms of a promise. In any case, it sets an expectation for an experience against which both the brand and the products need to deliver.
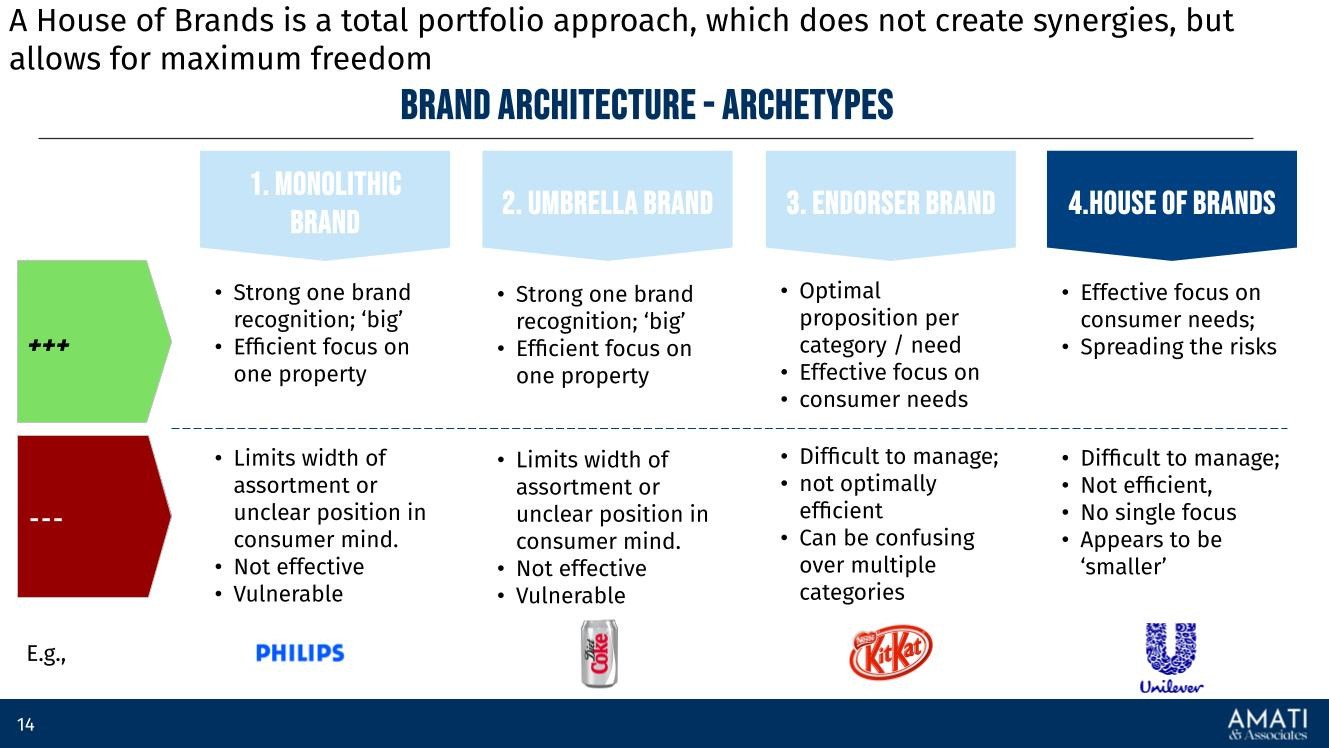
Brand Architecture: This involves defining the structure of the brand, including its portfolio, sub-brands, and their relationships. A clear brand architecture ensures consistency and clarity in brand messaging and positioning. For instance, The Coca-Cola Company has a well-defined brand architecture with its leading brand and various sub-brands like Diet Coke, Coca-Cola Zero Sugar, and Coca-Cola Life.
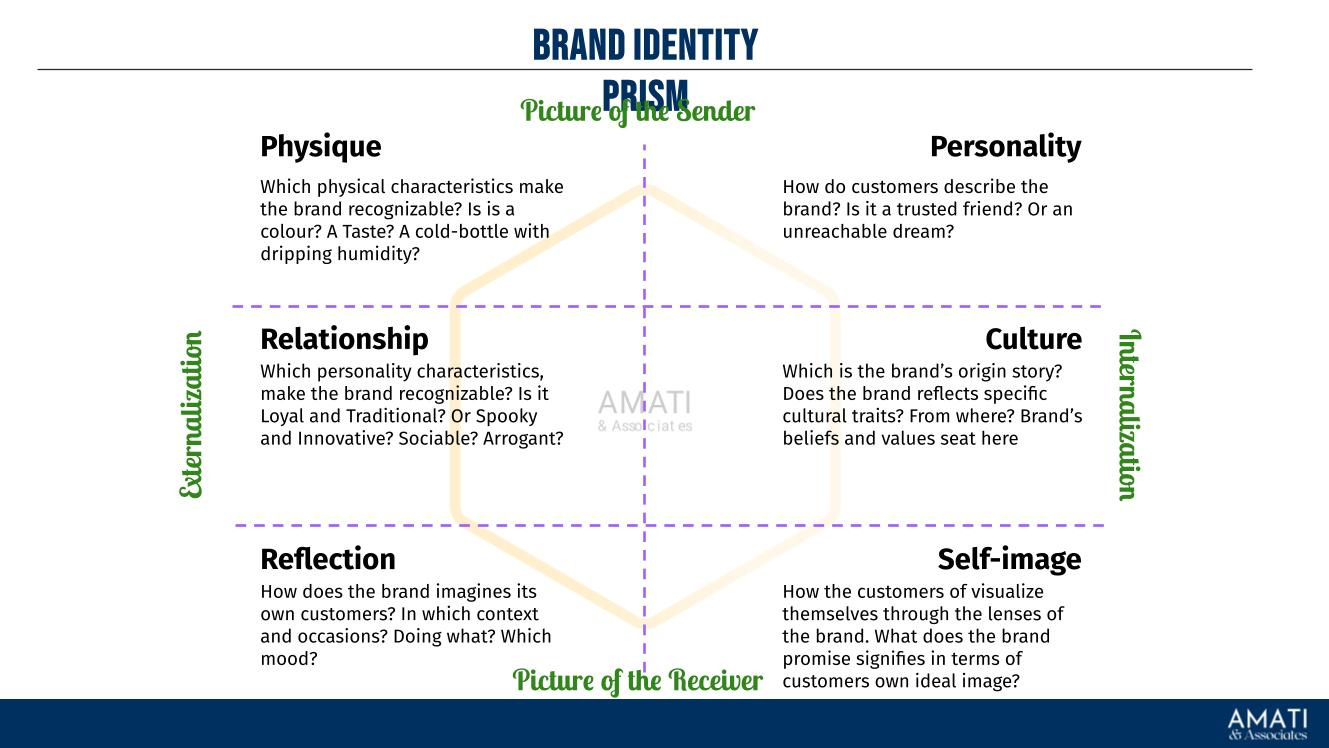
Brand Design: The visual and emotional elements of the brand create a connection with consumers. This includes logo design, packaging, and overall brand aesthetics. Effective brand design communicates the brand's values and differentiates it from competitors. Apple's minimalist and sleek brand design is a prime example of how effective brand design can create a solid emotional connection with consumers.
Brand Strategy Checklist
Is your brand strategy compelling? ………………………. ☑
Is your brand promise unique? ………………………. ☑
Is your brand based on insights ………………………. ☑
Does your brand architecture simplify the relationship between lines and categories? ………………………. ☑
Is your brand strategy easy to execute? ………………………. ☑
Is your brand strategy scalable? ..……………………. ☑
Is your brand design consistent with your positioning? ………………………. ☑
4Ps Marketing
The 4Ps—Product, Price, Promotion, and Placement—are fundamental to marketing strategy. This component of the model provides a detailed approach to each element:
Product: The product strategy focuses on quality, innovation, and differentiation. Understanding consumer needs and preferences helps develop products that meet or exceed expectations. Continuous innovation ensures the brand stays relevant and competitive. For instance, Dyson focuses on innovative technology and high-quality materials in its vacuum cleaners and other household products to differentiate itself from competitors.
Price: Pricing strategy is critical for market positioning. This involves determining the optimal price point that balances profitability and consumer demand. Various pricing strategies, such as penetration, premium, and competitive, can be employed based on market conditions and brand positioning. Apple uses a premium pricing strategy for its products, positioning them as high-end and exclusive. Pricing must consider the value chain, especially when dealing with indirect route-to-market and external partners, which is the most common case for consumer goods companies.
Promotion: Promotional strategies drive consumer awareness and sales. This includes advertising, sales promotions, public relations, and digital marketing. An effective promotional strategy uses various channels to reach the target audience and communicate the brand message. Coca-Cola's extensive advertising campaigns, including TV commercials, online ads, and sponsorships, effectively promote its brand globally.
Placement: Distribution strategies ensure that products are available to consumers where and when they want them. This involves selecting and managing distribution channels, including retail, online, and direct-to-consumer. Efficient distribution maximizes market reach and convenience for consumers. Amazon's extensive distribution network and efficient logistics system ensure the timely delivery of products to consumers worldwide.
4Ps Marketing Checklist
Are your product benefits compelling? ………………………. ☑
Is your pricing strategy balancing internal and external objectives? ………………………. ☑
Is your promotional approach unique ………………………. ☑
Does your distribution strategy fit your product and pricing? ………………………. ☑
Is your brand strategy easy to execute? ………………………. ☑
Is your brand strategy scalable? ..……………………. ☑
Is your brand design consistent with your positioning? ………………………. ☑
Inner Middle Layer
This layer includes links between strategic elements and executional ones.
Marketing Plan: A marketing plan is a comprehensive document or blueprint that outlines a company’s marketing efforts for the coming year(s). It describes business activities that accomplish specific marketing objectives within a set time frame. A marketing plan helps guide the direction of a company's marketing activities and ensures alignment with business goals. A marketing plan summarizes the brand strategy, the 4Ps approach, and a translation of those into activities for the following years. It, therefore, includes a budgeting part and a forecast of sales.
Media: Media plays a crucial role in communicating the brand message to the target audience. This includes traditional media (TV, radio, print) and digital media (social media, email marketing, content marketing). A well-integrated media strategy ensures consistent messaging across all platforms. Nike's use of social media campaigns, influencer partnerships, and traditional advertising effectively reaches and engages its target audience.
Segmentation: Market segmentation involves dividing the market into distinct groups of consumers with similar needs and characteristics. This allows for more targeted and effective marketing strategies. Segmentation can be based on demographics, psychographics, behavior, or geography. For example, Procter & Gamble segments its market for household cleaning products into different demographic groups, tailoring its marketing messages to each segment's specific needs and preferences.
Category Entry Points (CEPs) are situations or contexts prompting consumers to consider a specific product category. In the food and beverage industry, CEPS are usually called consumption occasions. For example, feeling thirsty might trigger thoughts of soft drinks or water. While CEPs drive substantial mental availability, marketers also use them to fuel the visibility and discoverability of products in the proper channels, positively impacting Physical Availability. A simple CEP framework:
Persona: The leading actor, the target consumer.
Motivation: Their interest or purchase includes functional needs and emotional desires.
Emotion: The consumer's emotional state at the point of engagement.
Locale: The physical or digital space where the transaction or engagement occurs.
Companionship: Identifying if the consumer is alone or with others and what that implies for the buying decision.
Activity: What the consumer does during the engagement, providing context to the consumption.
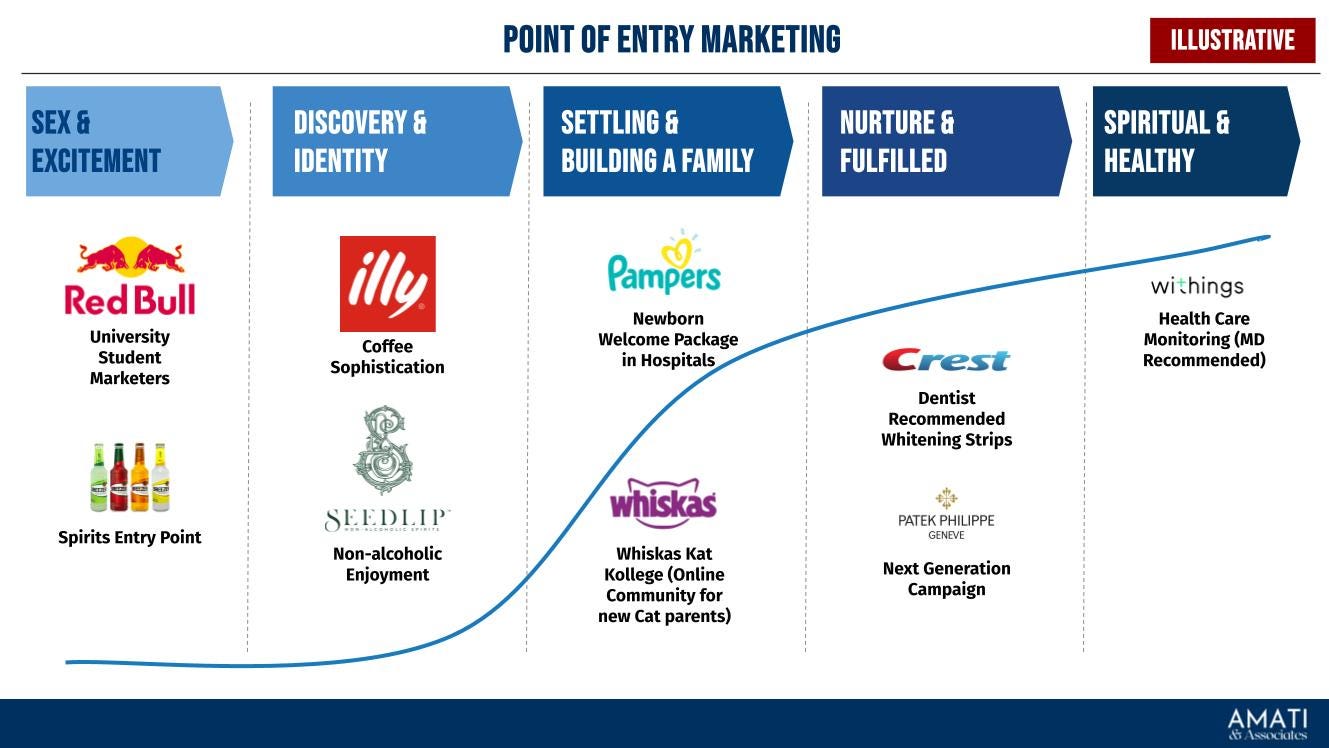
Point of Marketing Entry: When a consumer becomes open to a new product or category, often due to life changes. An example is starting a fitness regime, making someone more receptive to gym memberships or healthy foods. Many brands use in-gym visibility to reach the radar screen of prospective consumers interested in their offering (e.g., supplements, training accessories). PMEs are mostly related to life changes and life stages. These are typical questions necessary to identify a PME:
What life events or changes typically precede interest in our category or product? For Pampers, a newborn is an example.
At what moments do consumers realize they need a solution like ours? Example: Planning to buy a house and mortgage brokers.
Which information sources do potential customers turn to first when seeking solutions in our category? An example is Wedding Makagines, which is for wedding planners.
Which professionals recommend our category? Example: Healthcare prescription frameworks for health-related ailments.
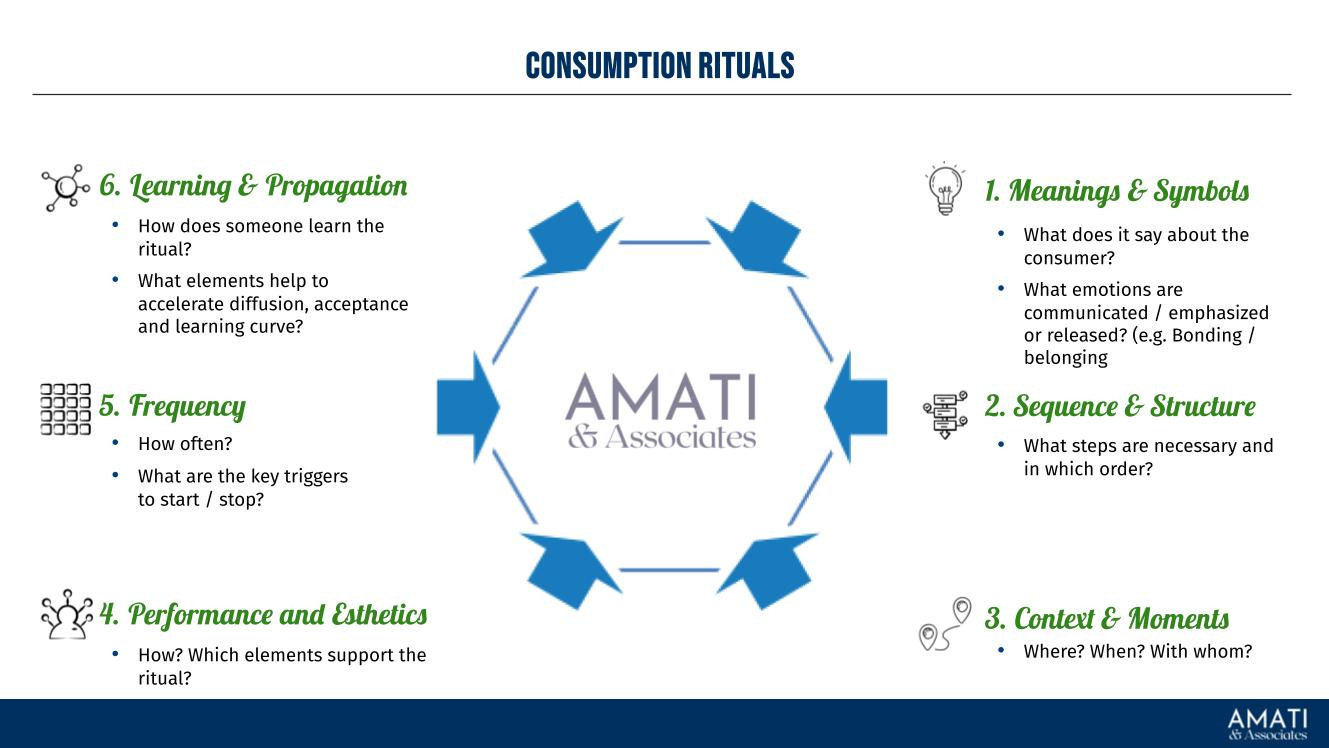
Rituals: Creating consumption rituals involves integrating the brand into consumers' daily lives through consistent and meaningful interactions. Rituals build emotional connections and foster brand loyalty. Starbucks has successfully created brand rituals around its coffee products, making them a part of consumers' daily routines.
Execution Focus: Effective execution of the brand strategy is paramount. This involves aligning all marketing activities with the brand's goals and ensuring consistent delivery across all touchpoints.
Integration and Execution
A cohesive marketing plan integrates all elements of the model, ensuring that data-driven insights and strategic elements align with marketing execution. Effective execution is critical for achieving marketing objectives and driving business success. This involves continuous monitoring, evaluation, and optimization of marketing activities. For example, Procter & Gamble integrates its external and internal data stacks, brand strategy, and 4Ps marketing to create a cohesive and effective marketing plan. By continuously monitoring market trends, competitor activities, and consumer preferences, P&G ensures its marketing strategies are aligned with its business goals and effectively executed across all touchpoints.
Conclusion
Master data to understand the category dynamics
Learn your business well. Especially master route to market and margins
Develop Executable Strategies